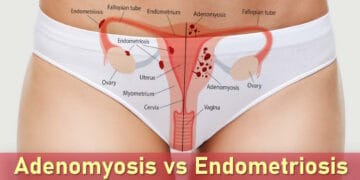
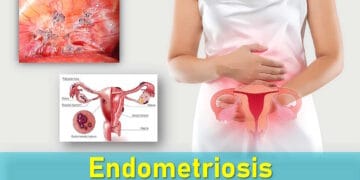
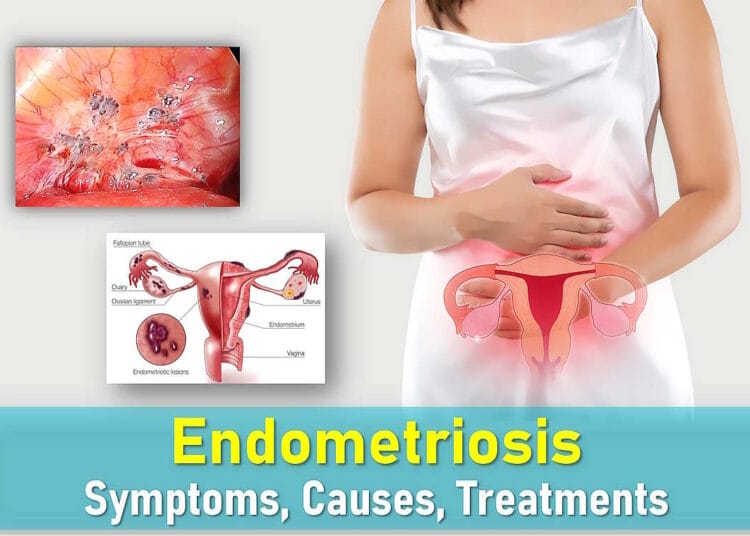
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) grows outside the womb, often in the pelvic region but sometimes in other areas of the body. Like the uterine lining, this tissue responds to estrogen, thickening and shedding with each menstrual cycle. However, because it has no way to exit the body, it can cause inflammation, scarring, and adhesions (where organs stick together).
Endometriosis is a chronic and often progressive disorder, meaning it can worsen over time. It is known for causing significant pain and may also lead to fertility challenges. The condition can disrupt daily life, affecting education, work, and physical activities. In the United States, endometriosis affects an estimated 1 in 10 women during their reproductive years, though many cases go undiagnosed due to mild or absent symptoms. While there is no cure, treatments are available to help manage symptoms effectively.
Who Is Affected by Endometriosis?
Endometriosis primarily impacts women of reproductive age, typically between 25 and 35 years old, though it has been diagnosed in girls as young as 11. It is rare after menopause. Certain factors may increase the risk, including:
- Family history (having a close relative with endometriosis)
- Early onset of menstruation or late menopause
- Never having given birth
- Having a low body mass index (BMI)
Research suggests that up to 50% of women struggling with infertility may have endometriosis, and it is a leading cause of chronic pelvic pain. Despite its prevalence, diagnosis often takes years due to varying symptoms and lack of awareness.
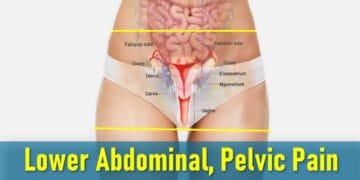
Common Locations of Endometrial Tissue Implants
In endometriosis, tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, forming what are called implants. These misplaced implants can develop in many different parts of the body, most commonly within the pelvic region:
- Ovaries: Endometrial implants often form cysts called endometriomas, or “chocolate cysts,” which may affect ovarian function and fertility.
- Uterine ligaments: These structures support the uterus, and endometrial growth here can contribute to pelvic pain or discomfort during movement or intercourse.
- The peritoneum: This is the thin membrane lining the abdominal and pelvic cavity, a common site for superficial endometrial lesions.
Less commonly, endometrial implants may appear in areas beyond the pelvic organs, including:
- Fallopian tubes: Implants can lead to scarring or blockage, interfering with the passage of eggs.
- Outer surfaces of the intestines: This may cause digestive symptoms such as bloating, cramping, constipation, or diarrhea.
- Bladder and ureters: Involvement of the urinary tract can result in painful urination, frequent urination, or even obstruction of urine flow.
- Rectovaginal space: The area between the vagina and rectum is another site where deep implants can form, leading to painful bowel movements or pain during sex.
In rare and more advanced cases, endometrial tissue can spread to locations outside the pelvic cavity, such as:
- The lungs (causing chest pain or difficulty breathing)
- The pericardium (lining around the heart)
- The cervix or vulva
- Surgical scars, such as those from C-sections or abdominal surgeries
Although these locations are unusual, they highlight how endometriosis is a complex condition that can affect multiple body systems, not just the reproductive organs.
Symptoms of Endometriosis
Endometriosis symptoms can vary widely from person to person. While some individuals may experience severe and life-altering discomfort, others may have no noticeable symptoms at all. In fact, many cases are only discovered during evaluations for infertility or other unrelated concerns. When symptoms do occur, they often depend on the location, depth, and extent of the endometrial-like tissue growth.
Common symptoms include:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain: Often most intense before and during menstruation. The pain may also occur during ovulation, intercourse, bowel movements, or urination. It can feel like cramping, sharp stabbing pain, or a dull, persistent ache.
- Painful periods (dysmenorrhea): Menstrual cramps that worsen over time and don’t respond well to typical pain relievers.
- Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia): Discomfort or cramping during or after sex, especially with deep penetration.
- Cramping or pain during bowel movements or urination: This is particularly common during menstruation and may be due to implants on or near the bladder or intestines.
- Heavy or irregular periods: Includes prolonged bleeding, clotting, or spotting between cycles.
- Pain radiating to the back, legs, or thighs: This may be linked to nerve involvement or deeper implants in the pelvic cavity.
- Gastrointestinal and urinary symptoms: These include bloating, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, frequent urination, or pain during urination. In rare cases, blood may appear in the urine during menstruation.
- Fatigue: Persistent low energy, especially during periods, is common and may be worsened by chronic pain and inflammation.
- Infertility: Around one-third of women with endometriosis face challenges conceiving. This may result from scarring, blocked fallopian tubes, impaired egg release, or inflammatory substances that disrupt fertilization or implantation.
Less common or rare symptoms may include:
- Low back pain that may intensify around menstruation.
- Chronic fatigue even outside of the menstrual period.
- Bloody urine or painful urination, especially if the bladder is involved.
- Chest pain, coughing blood, or pneumothorax (collapsed lung): Rare symptoms caused by endometriosis that has spread to the lungs.
- Neurological symptoms like headaches or seizures: Extremely rare, but possible if endometrial tissue is present in the brain.
It’s important to note that the intensity of the pain does not necessarily reflect the extent of the disease. Some individuals with severe endometriosis may have minimal symptoms, while others with milder stages experience intense, life-disrupting pain. This is partly due to:
- The location of implants, especially near dense nerve endings.
- Inflammatory substances released by the lesions that can trigger pain responses.
- Scar tissue formation that pulls or distorts surrounding organs and structures.
For many, the chronic and unpredictable nature of symptoms can interfere with work, school, relationships, and social life. This can also lead to emotional and psychological challenges such as anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal, emphasizing the need for a compassionate and comprehensive approach to care.
What Causes Endometriosis?
While the exact cause of endometriosis remains unclear, but several theories may explain how it develops:
- Blood or lymph system transport: Endometrial tissues may travel to other parts of the body through the blood or lymphatic systems, in a way similar to how cancer cells spread.
- Direct transplantation: After surgeries like a C-section or hysterectomy, endometrial cells might attach to the abdominal wall or other areas in the body.
- Genetics: Endometriosis appears to run in some families more than others, suggesting a possible genetic link.
- Reverse menstruation: Instead of exiting the body during a period, endometrial tissue flows backward into the fallopian tubes and abdominal cavity.
- Transformation: Other types of cells in the body may change into endometrial cells and begin growing outside the uterus.
How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing endometriosis can be challenging, with many women waiting 5 to 6.5 years between symptom onset and proper diagnosis. Some discover they have endometriosis while being evaluated for infertility or during unrelated surgeries.
Diagnostic Methods
- Medical history and physical exam: Your doctor will discuss your symptoms and perform a pelvic exam.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound or MRI scans may help identify endometrial growths.
- Laparoscopy: This surgical procedure allows doctors to view inside the pelvis and take tissue samples for confirmation. Considered the gold standard for diagnosis.
Stages of Endometriosis
To better understand and manage endometriosis, healthcare providers often classify the disease into four stages. These stages are based on factors such as the size, depth, and location of the implants, as well as the presence of scar tissue (adhesions) or ovarian cysts:
- Stage 1 (Minimal): A few small, superficial implants with little to no scar tissue.
- Stage 2 (Mild): More implants that are still relatively shallow, possibly with mild adhesions.
- Stage 3 (Moderate): Deeper implants are present, often along with small ovarian endometriomas and more significant scar tissue.
- Stage 4 (Severe): Extensive deep implants, large endometriomas on one or both ovaries, and dense adhesions that may affect surrounding organs.
Note that the stage doesn’t always correlate with pain levels, some with minimal endometriosis experience severe pain, while others with severe endometriosis may have few symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Consult your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Painful periods that interfere with daily life
- Pain during intercourse
- Difficulty conceiving
While treatments can help manage endometriosis, some women may experience recurring symptoms. Discuss all available options with your doctor to find the best approach for your situation.
Endometriosis Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for endometriosis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches typically involve medications, surgery, or a combination of both, depending on symptom severity and whether fertility is a concern.
Pain Management Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium are often the first line of defense against endometriosis pain. These medications:
- Reduce prostaglandin production (chemicals that contribute to pain and inflammation)
- Help relieve menstrual cramps and pelvic discomfort
- Don’t affect endometrial growths but can provide significant pain relief
Many women begin treatment with NSAIDs before receiving a formal endometriosis diagnosis. If these medications control symptoms effectively, further treatment may not be necessary.
Hormonal Therapies for Endometriosis
Since endometriosis responds to hormonal changes, several hormone based treatments can help manage symptoms:
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
These powerful medications:
- Temporarily stop ovarian estrogen production
- Create a menopausal like state that shrinks endometrial implants
- Are available as nasal sprays or injections
Potential side effects (often managed with “add-back therapy” using low-dose progesterone):
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood changes
- Bone density loss with long-term use
Progestin Therapy
Stronger than standard birth control pills, progestins like medroxyprogesterone acetate can:
- Reduce endometrial tissue growth
- Be an alternative for women who can’t take estrogen containing medications
Possible side effects include:
- Weight gain and bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Irregular bleeding
- Mood changes
Oral Contraceptives
Birth control pills are commonly prescribed to:
- Regulate or eliminate menstrual periods
- Reduce endometrial tissue growth
- Manage pain with continuous use (skipping placebo weeks)
Most women tolerate them well, though some may experience mild side effects like nausea or breakthrough bleeding.
Emerging and Specialized Treatments
Aromatase Inhibitors
These newer medications (like anastrozole and letrozole):
- Block estrogen production in endometrial implants
- Are typically used with other hormones in premenopausal women
- May cause bone loss with longterm use
Danazol (Rarely Used Today)
This synthetic hormone creates a high androgen, low-estrogen environment that can shrink implants but often causes significant side effects:
- Masculinizing effects (acne, facial hair growth, voice deepening)
- Weight gain
- Mood disturbances
- Liver concerns with longterm use
Most healthcare providers now reserve Danazol for special cases due to its side effect profile.
Surgical Options for Endometriosis
Surgery for endometriosis may be recommended when symptoms are severe or don’t respond to medication. There are two main surgical approaches:
Conservative Surgery
- Performed laparoscopically (minimally invasive)
- Preserves uterus and ovaries
- Removes or destroys endometrial implants using lasers or electrical current
- Helpful for restoring normal pelvic anatomy
Definitive Surgery
- Involves hysterectomy (uterus removal) with or without ovary removal
- Considered for severe cases when childbearing is complete
- Most effective for pain relief but doesn’t guarantee complete cure
About 40% of women experience endometriosis recurrence after conservative surgery. Many doctors recommend ongoing medical therapy post-surgery to prevent symptom return.
Potential Complications of Endometriosis
Endometriosis is more than just pelvic pain. It can lead to several short- and long-term health complications that may impact daily life and overall well-being:
- Bladder and bowel dysfunction: Endometrial tissue can grow on or near the bladder and bowel, causing symptoms like painful urination, constipation, diarrhea, or bloating. In some cases, pelvic floor physical therapy is recommended to improve muscle coordination and relieve symptoms.
- Chronic pain: Persistent pelvic, abdominal, or lower back pain is common and can significantly affect quality of life. Effective management often requires a multidisciplinary approach that includes gynecologists, pain specialists, physical therapists, and mental health professionals.
- Fertility challenges: Endometriosis is one of the leading causes of infertility, affecting approximately one in three women with the condition. Scar tissue, inflammation, or damage to reproductive organs can all play a role in reduced fertility.
Managing Endometriosis Complications
A personalized treatment plan is key to managing endometriosis-related complications. Depending on the severity of symptoms and your reproductive goals, options may include:
- Pelvic floor physical therapy: Helps reduce muscle tension and improve pelvic organ function.
- Pain management: Referrals to specialized pain clinics may provide access to medications, nerve blocks, or integrative therapies like acupuncture.
- Fertility treatments: Options such as ovulation-inducing medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help increase the chances of conception.
- Emotional and psychological support: Chronic pain and fertility struggles can take a toll on mental health. Support groups, counseling, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may be helpful.
Endometriosis and Fertility
Endometriosis can affect fertility in several ways, making conception more difficult for some women. Here’s how the condition may impact reproductive function:
- Blocked fallopian tubes: Scar tissue or adhesions may prevent eggs from traveling to the uterus.
- Ovulatory issues: Inflammation from endometriosis may interfere with the release of eggs or impair ovulation.
- Implantation problems: The uterine environment may be less receptive to embryo implantation.
- Egg or sperm quality: Inflammation and oxidative stress linked to endometriosis may affect the quality of eggs or sperm.
Many women with endometriosis are still able to conceive, especially with appropriate treatment. Fertility-enhancing options include:
- Laparoscopic surgery: Minimally invasive surgery can remove endometrial implants and improve fertility outcomes.
- Fertility medications: Drugs like Clomid or letrozole may help stimulate ovulation.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): IVF and other techniques can help bypass obstacles caused by endometriosis and support successful pregnancy.
Endometriosis and Other Health Conditions
Endometriosis is a systemic condition that may affect more than just reproductive health. Research shows that women with endometriosis may face increased risks for other health problems, including:
- Chronic pain conditions: Such as migraines, fibromyalgia, back pain, or interstitial cystitis (bladder pain syndrome).
- Other gynecological disorders: Including adenomyosis and uterine fibroids, which can cause heavy bleeding and pain.
- Systemic health issues: Studies suggest a possible link between endometriosis and autoimmune diseases (like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis), certain cancers (such as ovarian cancer), and cardiovascular conditions.
Living With Endometriosis
While there is currently no cure for endometriosis, certain strategies can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Hormonal therapies: Progestin-only pills, hormonal IUDs, or other medications can help suppress endometrial growth and manage symptoms.
- Breastfeeding: Prolonged breastfeeding may delay the return of menstruation and potentially ease endometriosis symptoms temporarily.
- Pregnancy: Some women experience symptom relief during pregnancy, although this is typically temporary and not a long-term treatment option.
Many women report significant symptom improvement after menopause due to the natural decline in estrogen. However, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may trigger recurrence in some cases. A comprehensive treatment plan, tailored to your symptoms, goals, and lifestyle—offers the best chance of long-term relief and improved quality of life.